In brief: What is the structure of hair and how does it grow? InformedHealth org NCBI Bookshelf
Table Of Content

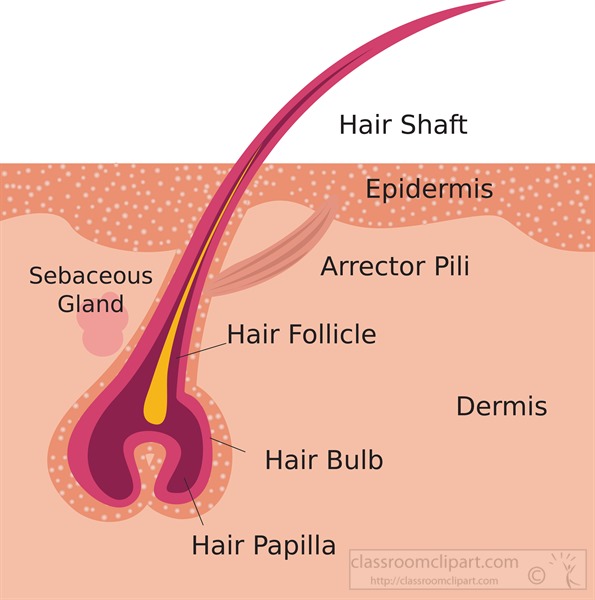
The hair follicle also contains melanocyte stem cells, which are located in the bulge and in the secondary hair [33–35]. The wall of the hair follicle is made of three concentric layers of cells. The cells of the internal root sheath surround the root of the growing hair and extend just up to the hair shaft. The external root sheath, which is an extension of the epidermis, encloses the hair root.
Do hair follicles heal after an injury and will my hair grow back?
This totals about five million hair follicles, with about one million on the head and 100,000 on the scalp. This is the largest number of hair follicles you will ever have. The bulb is a bulb-shaped, rounded structure at the bottom part of the hair follicle "stocking" that surrounds the papilla and the germinal matrix and is fed by blood vessels.
Blood supply
If you have any concerns about your hair growth, talk to a dermatologist. The immune system mistakes the hair follicles for foreign cells and attacks them. It can lead to alopecia universalis, which is a total loss of hair all over the body.
Figure 3: Hair follicle-associated myelinated nociceptors belonged to a... - ResearchGate
Figure 3: Hair follicle-associated myelinated nociceptors belonged to a....
Posted: Tue, 05 Dec 2023 15:54:26 GMT [source]
How do I strengthen my hair follicles?
This specialized immune environment of IP is required to prevent destructive immune reactions in critical regions. Other immune privileged sites include the anterior chamber of the eye, testis, brain and placenta. Hair follicle IP has a unique characteristic of recurring in a cyclic pattern. The sebaceous gland produces sebum, or oil, which is the body’s natural conditioner. More sebum is produced during puberty, which is why acne is common during the teen years. It protects your skin and traps particles like dust around your eyes and ears.
Structure of hair shaft under a microscope
Our team is growing all the time, so we’re always on the lookout for smart people who want to help us reshape the world of scientific publishing. You can help keep your hair healthy by taking care of your overall health. Eating nutritious foods is one way to improve hair from the inside out. Check with your doctor if you have questions on your hair’s growth and how it might be impacted by your health. An acute case is fairly common, lasts less than six months and in 95% of the cases it goes away. Typically it is caused by a stressful event that causes the telogen phase to begin prematurely and causes the hair to thin and fall out.
Scalp biopsies, hormone studies, and a potassium hydroxide examination for fungi may also need to be performed in certain cases. It is important to diagnose hair disease correctly, as the treatment for hair loss is dependent on the diagnosis. Once the hair follicle has developed in the fetus, lanugo hairs grow in utero. They eventually shed by about 36 to 40 weeks gestation and are replaced by vellus hairs that cover most areas of the body.
Alopecia areata
The function of hair in humans has long been a subject of interest and continues to be an important topic in society, developmental biology and medicine. The arrector pili muscle is the band of smooth muscle fibers that attach to the dermis and connective tissue layer of the hair follicle. It passes obliquely from the lower part of the hair follicle to the junction of the dermis and epidermis. The hair bulb represents the hair matrix, and hair follicles stem cells.

Again, this diagram shows different layers of rounded nucleated cells that form the outer root layer of the hair follicle. You will see a glassy membrane in the diagram that separates the inner root layer from the outer root layer. There is an inner root layer that remains inside the outer root layer. This layer contains the softer keratinized cells derived from the cells in the hair matrix. You will also find three layers in the composition of the inner root layer – Huxley’s layer, Henle’s layer, and the outer cuticle layer. Ectodysplasin (EDA) and its receptor (EDAR) are another important pathways involved in the placode stage of hair morphogenesis.
How to visualize the scales and medulla of hair?
The hair bulb is the lowest expanded extremity of the hair follicle that fits like a cap over the dermal hair papilla, enclosing it. The dermal hair papilla is a cluster of mesenchymal cells giving rise to several capillaries, which form a capillary loop. The dermis then grows upwards into the base of thefollicle to form the dermal papilla. This allows capillaries (blood vessels) to enter the papilla and provide nutrients for the hairshaft to grow. Again, the hair shaft shows three important features – cuticle, cortex, and medulla- that I have already described with the labeled diagrams.
From straight to curly, thick to thin: here's how hormones and chemotherapy can change your hair - The Conversation France
From straight to curly, thick to thin: here's how hormones and chemotherapy can change your hair.
Posted: Thu, 11 Jan 2024 08:00:00 GMT [source]
In humans, one function of head hair is to provide insulation and help the head retain heat. Head hair also protects the skin on the head from damage by UV light. One idea is that body hair helps to keep us warm in cold weather. When the body is too cold, the arrector pili muscles contract and cause hairs to stand up, trapping a layer of warm air above the epidermis. However, this is more effective in mammals that have thick hair or fur than it is in relatively hairless human beings. Hair is a filament that grows from a hair follicle in the dermis of the skin.
Now, let’s see the second diagram (schematic presentation), where the different layers of the hair follicle are seen. This diagram shows the hair root that contains the cuticle, cortex, and medulla. It also shows the Huxley’s layer and Henle’s layer that form the inner root layer of the hair follicle. Again, the arrector pili muscle lies on the side of the hair follicle and forms an angle with the skin surface.
You will find different secretory cells in the structure of the sebaceous gland of an animal’s skin. So, let’s know the specific identifying features of a hair under a light microscope. Here, I will enlist some important identifying features of hair and hair follicles for transverse and cross-sectioned samples.
The infundibulum is the portion from the invagination of the epidermis to the level of opening of the sebaceous gland. The infundibulum is part of the pilosebaceous unit where sebum is expressed. The isthmus extends deeper to the level of insertion of the arrector pili muscle. The arrector pili muscle has attachments to the hair follicle and adjacent dermis.
This process cuts the hair off from its blood supply and from the cells that produce new hair. When a club hair is completely formed, about a 2-week process, the hair follicle enters the telogen phase. Hair texture (straight, curly) is determined by the shape and structure of the cortex, and to the extent that it is present, the medulla. The shape and structure of these layers are, in turn, determined by the shape of the hair follicle. Hair growth begins with the production of keratinocytes by the basal cells of the hair bulb.
Again, the ruptured cells are continuously replaced by stem cells located at the edges of the glands. This article might help you to know the different features of a hair (shaft and follicle) under a light microscope with their concise description. Again, I will try to show you the hairs of different animals like rabbits, cats, and dogs with their specific features. The first sign of catagen is the termination of melanogenesis in the hair bulb. However, any apoptosis is occurred in dermal papilla due to the expression of suppressor bcl-2 [11].
The hair in the nose and ears, and around the eyes (eyelashes) defends the body by trapping and excluding dust particles that may contain allergens and microbes. Hair of the eyebrows prevents sweat and other particles from dripping into and bothering the eyes. Hair also has a sensory function due to sensory innervation by a hair root plexus surrounding the base of each hair follicle. Hair is extremely sensitive to air movement or other disturbances in the environment, much more so than the skin surface. This feature is also useful for the detection of the presence of insects or other potentially damaging substances on the skin surface. This is visible in humans as goose bumps and even more obvious in animals, such as when a frightened cat raises its fur.
Comments
Post a Comment